Loading
2025
Volume 3, Issue 1, p1-175
Articles published in this issue are Open Access and licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY NC) where the readers can reuse, download, distribute the article in whole or part by mentioning proper credits to the authors.
PDE4 inhibition and enhancement of human memory and cognition
Graeme B. Bolger
Two distinct, but intertwining, threads of inquiry have demonstrated that the PDE4, or cAMP-selective, phosphodiesterases, have an essential role in human cognition, learning and memory. Study of genetically-modified preclinical models, and of humans with mutations in the PDE4D gene, has provided some of the most rigorous proof of the importance of PDE4 signaling in the CNS. More recently, clinical trials of PDE4-selective inhibitors have shown promising clinical activity in disorders of cognition and memory.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p1-9 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.048
The extract of Nicotiana glauca induces apoptosis in rhabdomyosarcoma cells
Lucía Pronsato, Lorena Milanesi, Andrea Vasconsuelo, Natalia Frattini, Nicolás Blanco
Cancer is a leading cause of childhood mortality, with rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) being the most prevalent type diagnosed in approximately two-thirds of pediatric cancer cases, particularly the embryonal subtype. RMS represents the most common soft tissue sarcoma in children and adolescents, accounting for around 2-3.5% of all pediatric malignancies [1].
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p10-18 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.049
Cognitive impairment in hemodialysis needs sufficient attention
Jun Liu, Yani He, Kehong Chen
Hemodialysis is the most common form of kidney replacement worldwide. It is expected that the acceptance rate of hemodialysis will continue to increase in the coming decades [1]. About 89% of dialysis patients worldwide receive hemodialysis. The majority of these patients are living in high-income countries or middle to high-income countries such as Brazil and South Africa.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p19-22 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.050
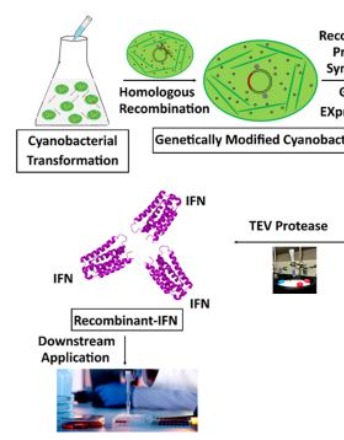
Recombinant protein synthesis and isolation of human interferon alpha-2 in cyanobacteria
Anastasios Melis, Bharat Kumar Majhi
Interferons (IFNs) are a class of small immunological proteins that are secreted by infected cells during viral or bacterial infections to combat and prevent infection propagation [1]. They play important roles in triggering signal cascade processes inside the cell that activate other immune cells and limit viral multiplication.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p23-26 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.051
Insights into early acne pathogenesis: Exploring intercellular dynamics and key dysregulated genes
Min Deng, Kiana Farahani, George W. Agak
Acne vulgaris, the most common skin condition worldwide, affects over 85% of adolescents, with nearly half continuing to experience it into adulthood. The Scarring and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation associated with acne can profoundly impact mental health and self-esteem, underscoring the importance of early and effective treatment [1].
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p32-39 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.053
Comment on “Hsa_Circ_0105596/FTO inhibits progression of Parkinson’s disease by sponging miR-187-3p and regulating eEF2”
Taoli Liu, Shumin Cheng, Qingqing Zhu
Parkinson’s disease (PD), a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, characterized by clinical features such as bradykinesia and resting tremor. It is characterized by specific neuropathological changes. These changes include the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra (SN) pars compacta.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p40-41 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.054
The role of stress granules in heavy metal-induced carcinogenesis
Rukayat Aromokeye, Megan Carver, Haining Zhu, Lei Wang
Stress granules (SGs) are dynamic, membraneless organelles that assemble in response to cellular stress, such as oxidative stress, hypoxia, or nutrient deprivation [1,2]. Protein translation typically is halted under stress conditions, leading to assembly of SGs containing mRNAs, RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), and other proteins.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p43-46 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.055
The role of circulating anti-aging αKlotho in cardiac aging
Dong I Lee, Dao-Fu Dai
Aging is an inevitable biological process that significantly affects various organs, including the heart. Cardiac aging, with its associated structural and functional changes, can lead to left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy, diastolic dysfunction, increased arterial stiffness, and reduced overall cardiac functional reserve [1,2].
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p54-58 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.057
The combination of TSPO ligands and CDK1 inhibitors may be a novel approach for the treatment of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor
Xingnan Zhang, Song Liu
MPNSTs are aggressive Schwann cell-derived sarcomas, frequently associated with NF1 mutations. Traditional treatments, including surgery and chemotherapy, are largely ineffective, highlighting the urgent need for novel therapeutic strategies. NF1 loss leads to RAS pathway activation, which in turn activates multiple signaling cascades, including RAF-MEK-ERK1/2, PI3K-AKT, and RalGDS pathways. Inhibition of these pathways has been explored, with MEK inhibitors, such as selumetinib, showing some promise in clinical trials (NCT03433183).
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p59-63 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.058
Sirt1-mediated deacetylation in MAFLD: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
Libang Chen, Qian Lu, Tingting Yang
Apart from alcohol and other definitive factors, metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), formerly known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is a clinicalpathological syndrome characterized by hepatic steatosis and lipid accumulation.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p69-75 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.060
A new role of dopamine receptor D2 agonist ropinirole: Targeting NAT10 for treating periodontitis
Jiahui Tan, Jialei Wu, Lufei Wang
Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects more than 40% of the adult population aged over 30 years in the United States, indicating a high prevalence [1]. It impairs the integrity of the tooth-supporting tissue with clinical manifestations featured of gingiva bleeding, periodontal ligament degradation, and alveolar bone resorption. Periodontitis is a multifactorial disease, involving interactions of bacterial pathogens, host immune responses and environmental factors such as smoking [2].
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p76-79 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.061
Complex actions of amyloid beta on hippocampal neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis
Jaehoon Song, Inhee Mook-Jung
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive cognitive decline and memory impairment. One of the key pathological hallmarks of AD is the accumulation of amyloid beta (Aβ), a peptide derived from the sequential cleavage of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) by β- and γ-secretases .
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p80-84 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.062
Engineered Ag135Cu60 nanoclusters with buckminsterfullerene topology: Structure and optical dynamics
QiKai Han, Li Tang, Shuxin Wang
Metal nanoclusters, serving as a mesoscopic bridge between discrete atoms and bulk materials, have emerged as a frontier in the convergence of coordination chemistry and material science.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p85-89 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.063
Regulating ferroptosis by glutathione s-transferases: From mechanistic to potential therapeutic targets
Yanyun Shi, Qi Yao
Ferroptosis is a type of cell death caused by iron-dependent lipid peroxidation. In recent years, certain isoforms of glutathione-S-transferases (GSTs) have been identified that may play a key role in regulating ferroptosis. Previous study demonstrated that the NRF2/GSH/GST/RLIP76 and MRP1 axis acts as an independent anti-ferroptosis pathway. Furthermore, this study evaluated the therapeutic potential of mifepristone (RU486) for mitigating acetaminophen (APAP)-induced liver injury in vivo.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p90-94 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.064
Beyond single targets: Crosstalk between endoplasmic reticulum stress, ferroptosis, and vitamin D signaling in stroke treatment
Yifeng Zhang, Xiaolu Wang, Zimeng Chen, Yanqiang Wang
Stroke remains a leading cause of death and long-term disability worldwide, with ischemic stroke representing approximately 85% of all stroke cases. Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury significantly exacerbates neuronal damage through mechanisms such as oxidative stress, ferroptosis, and endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS).
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p95-102 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.065
Revisiting the effects of curcumin on postmenopausal women’s health—insights from a systematic review and meta-analysis
Dachuan Jin, Shunqin Jin
The myriad health issues triggered by hormonal changes in postmenopausal women have garnered increasing attention in recent years. Among various nutraceuticals and phytoestrogens, curcumin—a bioactive compound derived from Curcuma longa—has emerged as a promising candidate due to its favorable safety profile, multi-targeted biological activities, and growing evidence supporting its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and metabolic benefits.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p103-105 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.066
Gut microbiota-immunity interaction and personalized immune response
Chien Dinh Huynh
As presented in our previous article, the human immune system is built upon a genetic framework passed down through countless generations. Traditional dietary habits rooted in specific ethnicities have fostered profound immune diversity, enabling adaptation to harsh environmental conditions and ultimately ensuring survival. Consequently, it’s evident that each individual’s immune characteristics are uniquely shaped by a combination of racial background, environmental exposure, and dietary practices.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p106-110 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.067
NCAM1: A newly discovered immune checkpoint in molluscs and its functions in immune regulation
Muchun He, Renle Chang, Jiejie Sun, Linsheng Song
Natural killer cells (NK cells), a unique subset of cytotoxic lymphocytes, play pivotal roles in immune defense through directly recognizing and eliminating pathogen-infected cells or cancer cells. Currently, NK cells have been identified in humans, mice, and teleost fishes. However, the existence, identification and functional characterization of NK-like cells in invertebrates remain poorly understood. Studies in Drosophila [6] and shrimp [7] had revealed that their undefined type of hemocytes analogous to vertebrate NK cells had direct cytotoxic activity against invading pathogens or abnormal cells.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p111-114 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.068
Hepatic stellate cells as RSPO3-Wnt/β- catenin hubs governing liver zonation and regenerative capacity
Qiang Yang, Chunsheng Lin, Ying Cai, Chao Wang, Zhibo Wang, Sifan Guo, Shi Qiu, Aihua Zhang
The liver emerges as an ultimate metabolic nexus—a polyfunctional organ that simultaneously performs biochemical detoxification, macromolecular processing, and systemic nutrient governance. While hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) were historically confined to their fibrogenic identity, their broader homeostatic orchestration remained enigmatic. RSPO3 as a linchpin in hepatocyte dynamics, with targeted pharmacological modulation enhancing hepatic lobular repatterning, regenerative capacity, and metabolic optimization.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p119-122 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.070
From mitosis to mutagenesis: Chromosomal passenger proteins at the crossroads of replication stress and cancer resilience
Shirley K. Knauer, Roland H. Stauber
The chromosomal passenger complex (CPC), comprising Survivin, Aurora B kinase, INCENP, and Borealin, is classically known for its essential functions during mitosis. However, recent findings expand the CPC's role beyond cell division, uncovering novel functions in replication stress response and genome stability maintenance.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p123-129 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.071
Chemokine-like Orion presentation as a potential switch in phagocytic signaling pathway activation during neuronal remodeling
Charline Gal, Clarisse Perron, Jean-Maurice Dura, Ana Boulanger
Immature nervous systems are initially overpopulated with neurons. A crucial step of remodeling that removes inappropriate connections is required and performed predominantly by phagocytic glial cells. The Drosophila chemokine-like Orion tags axons to be eliminated. Could the way Orion is presented by neurons be the critical factor in modulating subsequent intracellular glial responses?
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p135-140 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.074
Targeting inflammation in progeria – insights from combined baricitinib and lonafarnib treatment in a mouse model of progeria
Moritz Schroll, Karima Djabali
Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome (HGPS) is a rare and fatal premature aging disorder caused by progerin accumulation, leading to nuclear abnormalities, systemic inflammation, and early cardiovascular decline. Lonafarnib, a farnesyltransferase inhibitor (FTI), improves nuclear shape and extends lifespan, but its efficacy is limited and accompanied by pro-inflammatory effects. Here, we discuss preclinical findings from a combination therapy using the JAK1/2 inhibitor baricitinib (BAR) with FTI in a progeria mouse model.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p141-146 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.075
Angiotensin-(1-7) steers macrophages to inflammation resolution
Simone de Araújo, Erick Bryan de Sousa Lima, Lirlândia P. Sousa, Mauro Martins Teixeira
Angiotensin-(1-7) [Ang-(1-7)] is a biologically active peptide of the renin–angiotensin system (RAS) that counterbalances the actions of angiotensin II (Ang II), primarily through binding to the Mas receptor (MasR). This axis exerts significant immunomodulatory effects by influencing several features of leukocytes, including macrophage function, a central component in the resolution of inflammation. Macrophages contribute to tissue homeostasis by clearing apoptotic cells, releasing anti-inflammatory mediators and supporting tissue repair.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p147-152 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.076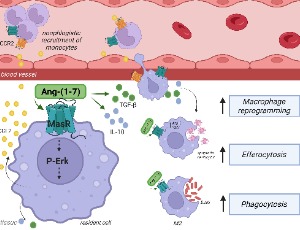
Neuroimmune interplay in peripheral neuropathies
Xiangyun Yao, Cunyi Fan, Song Guo Zheng
The interplay between neural cells and immune cells is a determinant factor for microenvironment restoration following nerve injury. Nerve-resident immune cells respond microenvironment signals and switch to pro-inflammatory or pro-regenerative phenotype. These phenotypes have different effects on axon regeneration. Early-phase neuroinflammation clears debris and remodels a permissive microenvironment for nerve repair. However, persistent and overactive inflammation is destructive and detrimental to regeneration. Despite all this information, our understanding of neuroimmune interplay in traumatic and diabetic neuropathies remains poor.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p153-157 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.077
Confine to create: ER-endosome contacts foster autophagy initiation
Juliane Da Graça, Etienne Morel
Autophagy is a conserved cellular process in which eukaryotic cells degrade and recycle intracellular material via a dedicated trafficking toward lysosomes. Under starvation, autophagy is initiated by the formation of a double-membrane organelle called the autophagosome, which originates from the closure and maturation of a transient membrane structure known as the phagophore. The precise membrane source of the phagophore and the mechanisms underlying its biogenesis remain incompletely understood.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p158-162 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.078
Dual roles, targeting dilemmas, and future priorities: Rethinking METTL-mediated m6A modification in head and neck cancer
Ming Yang, Han Zhu, Zile Zhang, Xuexia Liu, Hua Zhang, Gang Qin
With the recently published review in Cellular Signaling, we highlight the importance of Methyltransferase-like (METTL) family-mediated N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in head and neck cancer (HNC) progression, providing a theoretical foundation for their potential use as therapeutic targets.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p163-167 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.079
Insights into the methyltransferase activity and methylation status of PRDM16 in malignant tumors
Yu Wang, Yuting Wang, Anjia Han
The PRDM16 (PRDI-BF1-interacting and RIZ1-homologous domain 16) participates in a range of biological processes including tumorigenesis. The protein regulates gene transcription through intrinsic chromatin-modifying enzymatic activity or by forming complexes with histone modifications or other nuclear proteins. Accumulating evidence indicates that the methyltransferase activity and its methylation status of PRDM16 had been further studied.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p168-172 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.080
Insulin or islet: That’s the question
Byung-Joon Kim, Hee-Kyeong Park, Jun-Seop Shin, Jin Kuk Kim, Kwang-Won Kim
This commentary discusses our recent findings that, contrary to the β-cell rest hypothesis, early short-term insulin administration in a mouse model of marginal β-cell deficiency paradoxically worsened glycemic control and induced adverse α-cell-mediated islet remodeling. Early insulin intervention is hypothesized to preserve β-cell function; however, its utility in marginal β-cell deficiency is not well-established.
Cell Signal, 2025, Volume 3, Issue 1, p173-175 | DOI: 10.46439/signaling.3.081
Recommended Articles
EGCG modulates nuclear formaldehyde-induced Tau phosphorylation in neuronal cells
Tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease is known to hamper several cellular functions including microtubule dynamics, proteostasis etc. Tau is a microtubule-stabilizing protein, playing an important role in maintaining the integrity of the axonal microtubules [1,2].
Review of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: Challenges, diagnostics, management, and pathophysiology
Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae (sdAVFs) are rare (5-10 per million per year), often misdiagnosed vascular lesions most commonly found in the thoracolumbar spine [1-7]. These lesions commonly present with progressive myelopathy in male (approximately 80%) patients who are usually in their 7th decade of life [3-6,8].
Perspective study of UPR signaling molecules as potential biomarkers in bone metabolism
The skeletal system consists mostly of extracellular matrix and mineral salts. Osteoblasts and chondrocytes create enormous amounts of extracellular matrix proteins for skeletal systems to grow and sustain. Many skeletal metabolism related proteins are produced by endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and secrete outside cell membrane then form to extracellular oligometric matrix proteins and collagens.
Selecting ideal combined immunotherapy for treating HCC
The discovery of proper sensitizers for immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) treatment represents a significant breakthrough in the field of cancer therapy, but it is still in initial stage [1,2].
Radiation induced molecular signalling in the cells: A real struggle between death or breathe
Radiation is omnipresent in the universe. Since the primitive period, chemical evolution led to a biological evolution somehow driven by the ionizing and non-ionizing radiation on the Earth’s atmosphere [1,2].
Approach to testicular adrenal rest tumors in children and adolescents with congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a disorder affecting cortisol biosynthesis in the adrenal cortex [1]. 21-hydroxylase deficiency is the most frequent reason for CAH, with an incidence between 1:10.000 and 1:20.000 [2]. Due to the lack of enzyme function, patients with any enzyme deficiency cannot synthesize cortisol effectively.
Aiming for the brain: a new thermogel-based drug delivery platform
The design of safe drug delivery systems that locally allow efficacious concentration of curative molecules has become the latest frontier in nanomedicine. It usually relies on the entrapment of drugs into micro/nano carriers guaranteeing for the controlled release of the drugs while protecting them from degradation and fast clearance.
Do arrestin oligomers have specific functions?
Arrestins were discovered as key players in the conserved two-step homologous desensitization of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs): they specifically bind active phosphorylated GPCRs, precluding their coupling to cognate G proteins, thereby stopping (“arresting”) G protein-mediated receptor signaling [1].
Immune-enhanced nanocomposites provide hope for drug-resistant infection treatment
Antibiotic misuse contributes to the emergence of multidrug-resistant organisms, resulting in infections that cause over one million deaths annually [1-3]. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop new antimicrobial methods. Traditional antibiotic therapy is often incomplete due to the emergence of drug-resistant strains, leading to relapse.
Deciphering Notch signaling notch by notch
The NOTCH receptors are mechanosensing proteins that require cell-cell contact and physical force for activation. While most receptors have evolved to respond to one or a few unique ligands, the four NOTCH receptors can respond to any of the five Delta/Serrate/Lag-2 (DSL) ligands - Jagged (JAG) 1, 2, and Delta-like (DLL) 1, 3, 4 [1].
A vicious cycle happened in the progress of hyperhomocysteinemia, the same may exist in the development of cancer
Homocysteine (Hcy) metabolism is at the intersection of two metabolic pathways: remethylation and trans-sulfuration, which abnormality can result in hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy). In the past few years our team has been working on the molecular mechanism of HHcy development.
The value of EGFR in individualized treatment for brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a member of the ErbB family. It is involved in biological processes such as cell proliferation, angiogenesis, inhibition of apoptosis, adhesion, metastasis, and is associated with the progression of lung cancer [1-3].
Development of an authentic light-activated calcium channel
Optogenetics utilizes the fusion of naturally occurring light-sensing proteins with target proteins to induce conformational changes, oligomerization, or dissociation in response to illumination of light with specific wavelengths.
GABA fluctuations driven by astrocytic Glu-GABA exchange explain synaptic acuity
Gliocentric paradigms showcase functional association of neurons with astrocytes, as in tripartite glutamatergic synapses. Astrocytes, activated by Glu:3Na(+) symport apply GABAergic inhibitory feedback on synaptic excitation via GABA efflux by GAT-3 reversal and subsequent GABAA activation (astrocytic Glu/GABA exchange [1-3]).
Commentary: Role of estrogen receptor β in kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) has become a growing global health challenge, impacting over 800 million individuals worldwide [1]. Numerous evidences have shown that women are more resistant to CKD than men before menopause, however this beneficial effect is diminished in those with post-menopause, highlighting the pivotal role of estrogen in kidney disease [2-5].
In search for molecular mechanisms of Post COVID-19 vascular damage
Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the world has changed significantly with newchallenges constantly arising (Figure 1) [1]. One of the main challenges is the increased prevalence of a prolonged post-COVID-19 syndrome, widely known as "Post COVID", which is currently regarded as a public health issue worldwide [2].
Pathogenic contribute of unaffected cardiac cells in female Fabry cardiomyopathy
Cardiac hypertrophy is one of the most common manifestations of Fabry disease (FD) [1] and it can be the only clinical expression, in the so called cardiac variant, as result of specific mutation of
alpha-galactosidase-A gene (GLA), as the N215S one [2].
Probes for cancer metastasis imaging and therapeutic targeting
Metastasis of cancer is the process by which the primary tumor spreads from the original site to other parts of the body. Palliative care is the most common treatment option available for patients with metastatic cancer, but most patients eventually succumb to the disease due to the lack of therapeutics that can specifically target disseminated tumors [1].
Unlocking the significance of CD226 in cancer
CD226 is a transmembrane glycoprotein with a well-defined structural organization, which is primarily expressed on natural killer (NK) cells, cytotoxic T cells, and some subsets of B cells [1,2]. Its primary structure consists of an extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic tail [1]. Each of these domains contributes to the protein's overall function.
Friend or foe? The elusive role of ANGPTL4 in inflammation
Angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4) is a multifaceted secreted protein discovered by three different institutions in 2000 simultaneously [1]. It is expressed in adipose tissues, liver, muscle, heart, kidney, skin, and other tissues. The nutritional, metabolic, and inflammatory status of the organism regulate the expression of ANGPTL4 [2-4].
